polarimeter principle and instrumentation|different types of polarimeter : vendor Traditionally, a sucrose solution with a defined concentration was used to calibrate polarimeters relating the amount of sugar molecules to the light polarization rotation. The International Commission for Uniform Methods of Sugar Analysis (ICUMSA) played a . See more 8 de dez. de 2022 · Um trabalhador de uma empresa de telecomunicações recebeu uma forte descarga elétrica nesta quarta-feira (7) em Bauru (SP) enquanto fazia manutenção de cabos de internet e ficou gravemente .
{plog:ftitle_list}
web11 de jul. de 2023 · Temos milhares de clipes e vídeo gratuitos na biblioteca - conheça todos os recursos do banco de imagens e vídeos. Pixabay is a vibrant community of creatives, .
A polarimeter is a scientific instrument used to measure optical rotation: the angle of rotation caused by passing linearly polarized light through an optically active substance. Some chemical substances are optically active, and linearly polarized (uni-directional) light will rotate either to the left (counter . See more
Polarization by reflection was discovered in 1808 by Étienne-Louis Malus (1775–1812). See moreThe polarimeter is made up of two Nicol prisms (the polarizer and analyzer). The polarizer is fixed and the analyzer can be rotated. The prisms . See moreLaurent's half-shade polarimeterWhen plane-polarised light passes through some crystals, the velocity of left-polarized light is different from that of the right-polarized light, thus the crystals are said to have two refractive indices, i.e. double refracting. See moreTraditionally, a sucrose solution with a defined concentration was used to calibrate polarimeters relating the amount of sugar molecules to the light polarization rotation. The International Commission for Uniform Methods of Sugar Analysis (ICUMSA) played a . See more
The ratio, the purity, and the concentration of two enantiomers can be measured via polarimetry. Enantiomers are characterized by their property to rotate the plane of See morePolarimeters measure this by passing monochromatic light through the first of two polarising plates, creating a polarized beam. This first plate . See more
The angle of rotation of an optically active substance can be affected by:• Concentration of the sample• Wavelength of light passing through the sample (generally, . See moreA polarimeter is an instrument used to determine the angle through which plane-polarized light has been rotated by a given sample. You will have the opportunity to use a polarimeter in .
A polarimeter is an optical instrument for accurately measuring the angle by which the polarization direction of light is rotated in an optically active medium.
A polarimeter is an instrument which measures the angle of rotation by passing polarized light through an optically active (chiral) substance. To measure . Principles of Polarimetry. Polarimetry measures the rotation of polarized light as it passes through an optically active fluid. The measured rotation can be used to calculate the . In this article, we will explore how a polarimeter works and its various applications in different fields. How Does a Polarimeter Work? A polarimeter works on the principle of .
If it is a liquid, the sample may be placed in the tube as a pure liquid (its is sometimes called a neat sample). Usually, the sample is dissolved in a solvent and the .Polarimetry is an instrumental analytical technique that uses rotation of polarized light (i.e. optical activity) by some substances as a measure of their concentration in a solution or other . An easily constructed and inexpensive polarimeter with an optical rotation angle resolution of about 0.5° is presented. It is made from small pieces of polarizing film, 2 LEDs, a protractor, and a few wires, all held in place with .Rudolph Research Analytical 55 Newburgh Road Hackettstown, NJ, 07840 USA Phone: 973-584-1558 Fax: 973-584-5440 [email protected]
Fluorimetry: Principle, Instrumentation, Factors, Uses. April 27, 2024 by Agrani Paudel. Fluorimetry is a scientific and analytical technique used to detect and measure the fluorescent light emitted by the sample (lying in the . Principles of Polarimetry A polarimeter consists of a polarized light source, an analyzer, a graduated circle to measure the rotation angle, and sample tubes. The polarized light passes through the sample tube and exhibits angular rotation to the left (-) or right (+).A polarimeter refers to an optical instrument used to determine the polarization properties of light beams and samples. . followed by a hybrid coupler and then the detectors. Although more complicated in principle, such a polarimeter could be implemented entirely on a single lithographed chip. . Basic mechanisms and instrumentation for . In measuring optical rotation, plane-polarized light travels down a long tube containing the sample. If it is a liquid, the sample may be placed in the tube as a pure liquid (its is sometimes called .
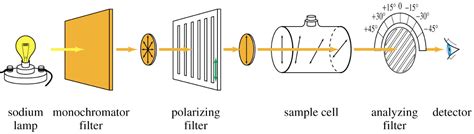
12.2 Principle Polarimetry is based on the fact that when a polarized light passes through the sample . 12.9 Instrumentation The polarimeter is a device used to measure the effect of optically active compounds on plane-polarized light. The components of polarimeter are: D OLJKW VRXUFH XVXDOO\ D VRGLXP ODPS Polarization is a basic property of light and is fundamentally linked to the internal geometry of a source of radiation. Polarimetry complements photometric, spectroscopic, and imaging analyses of .
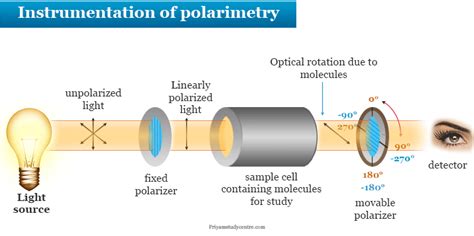
The document outlines the principles of polarimetry using optically active compounds and the instrumentation of a polarimeter. Applications of polarimetry include identification of compounds, determination of optical activity, and uses in the chemical, food, beverage, pharmaceutical, and sugar industries for purity testing and concentration .Polarimeter Figure 1 shows a principle of a polarimeter set up and its main components together with their function. Unpolarized light from the light source is first polarized. This polarized light passes through a sample cell. If an optical active substance is in a sample tube, the plane of the polarized light waves is rotated. TheBy reducing the path length of the sample cell from 100 mm to e.g. 2.5 mm or reducing the concentration of the sample, the result will be compatible with the measuring range of the polarimeter. In order to determine the specific rotation of a substance, the MCP polarimeter can use a shorter sample cell than 100 mm.A polarimeter is a scientific instrument used to determine the angle of rotation caused by an optically active material moving through polarized light. As the angle of rotation is defined, the degree by which the light is rotated. Basically, the angle of .
POLARIMETER. polarimetry: • Is an instrumental analytical method using rotation of polarized light by some substances as measure of their concentrationin a solution. • The instrument used is calledpolarimeter. Principle of polarimeter : • Un-polarized light from the light source is first polarized. • This polarized light passes through a sample cell.
why polarimeter is used
Principle of Spectrophotometer. The spectrophotometer technique is to measure light intensity as a function of wavelength. It does this by diffracting the light beam into a spectrum of wavelengths, detecting the intensities with a charge-coupled device, and displaying the results as a graph on the detector and then on the display device. 13. POLARIMETER Principle :Polarimeter measures the rotation of polarised lights as it passes through an optically active fluid. The measured rotation can be used to calculate the value of solution concentrations. .
polarimetry - Download as a PDF or view online for free. 19. SPECIFIC ROTATION: It is defined as the rotation produced by a solution of length 10cm & unit concentration (1gm/ml) for given wavelength of light at the .In a polarimeter (figure 2), plane-polarized light is introduced to a tube (typically 10 cm in length, figure 3) containing a solution with the substance to be measured. If the substance is optical inactive, the plane of the polarized light will not change in orientation and the observer will read an angle of [α]= 0 o. If the compound in the . Principle of Colorimeter. When an incident light beam with intensity I 0 passes through a solution, a part of the incident light is reflected (I r) and absorbed (I a) while the remaining incident light is transmitted (I t).. i.e., I o = I r + I a + I t. The measurement of (I 0) in the colorimeter eliminates (I r), and it is sufficient to calculate the (I a).Using cells with the same .
Homemade polarimeter in use. Video credit: David Whyte/YouTube Components and Types. Polarimeters have two polaroid plates mounted apart. The lower plate is generally fixed and known as the polarizer.The upper plate can be rotated and is known as the analyzer.Polarimeters have two Nicol prisms, a type of polarizer.
Turn on the polarimeter and allow it to warm up for 30 minutes. Fill the polarimeter cell with a solvent that has a known specific rotation value. Place the cell in the polarimeter and adjust the polarimeter until the reading matches the known specific rotation value of the solvent. Repeat the process with the same solvent to ensure accuracy. Mass Spectrometry (MS)- Principle, Working, Parts, Steps, Uses September 17, 2022 March 4, 2022 by Sagar Aryal Mass Spectrometry (MS) is an analytical chemistry technique that helps identify the amount and type of chemicals present in a sample by measuring the mass-to-charge ratio and abundance of gas-phase ions.A simple polarimeter to measure this rotation consists of a long tube with flat glass ends, into which the sample is placed. At each end of the tube is a Nicol prism or other polarizer. Light is shone through the tube, and the prism at the other end, attached to an eye-piece, is rotated to arrive at the region of complete brightness or that of . Polarimeter - Download as a PDF or view online for free. 16. SOURCE OF ERRORS The angle of rotation of an optically active substance can be affected by: Concentration of the sample Wavelength of light passing through the sample (generally, angle of rotation and wavelength tend to be inversely proportional) Temperature of the sample (generally the two .
1. Clean the polarimeter tube, beaker, flask and measuring cylinder with water. 2. Fill the polarimeter tube with distilled water. As you rotate the analyzer through 3600, you observe four uniform illumination positions- two of these are weak in intensity and the other two are strong. Choose one of the weak Key Factors to Select the Suitable Type of Polarimeters. Selecting the suitable type of polarimeter involves considering various factors to ensure accurate and reliable measurements for a specific application.. 1. Application and Purpose. Identify the primary purpose of using the polarimeter.Different types of polarimeters may be required for different .
custom moisture meter drywall
What are Conducting Polymers? As the name suggests organic polymers that conduct electricity are known as conducting polymers. They are also known as intrinsically conducting polymers (ICPs) and they have alternating single and double bonds along the polymer backbone (conjugated bonds) or that are composed of aromatic rings such as Phenylene, .
l is the length of the polarimeter tube in metres . d. is the relative density of the liquid or solution at 20 C . c. is the concentration of the solute expressed in grams per mL of solution . p. is the concentration of the solute expressed in gram per gram solution . Wavelength
webLionel Messi and Argentina will play exhibitions against Ecuador on June 9 at Chicago's Soldier Field and Guatemala five days later at FedEx Field in Landover, Maryland, ahead .
polarimeter principle and instrumentation|different types of polarimeter